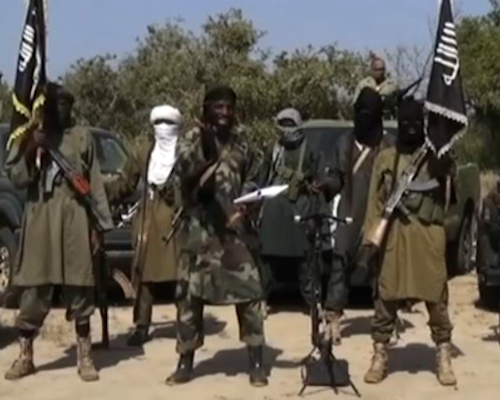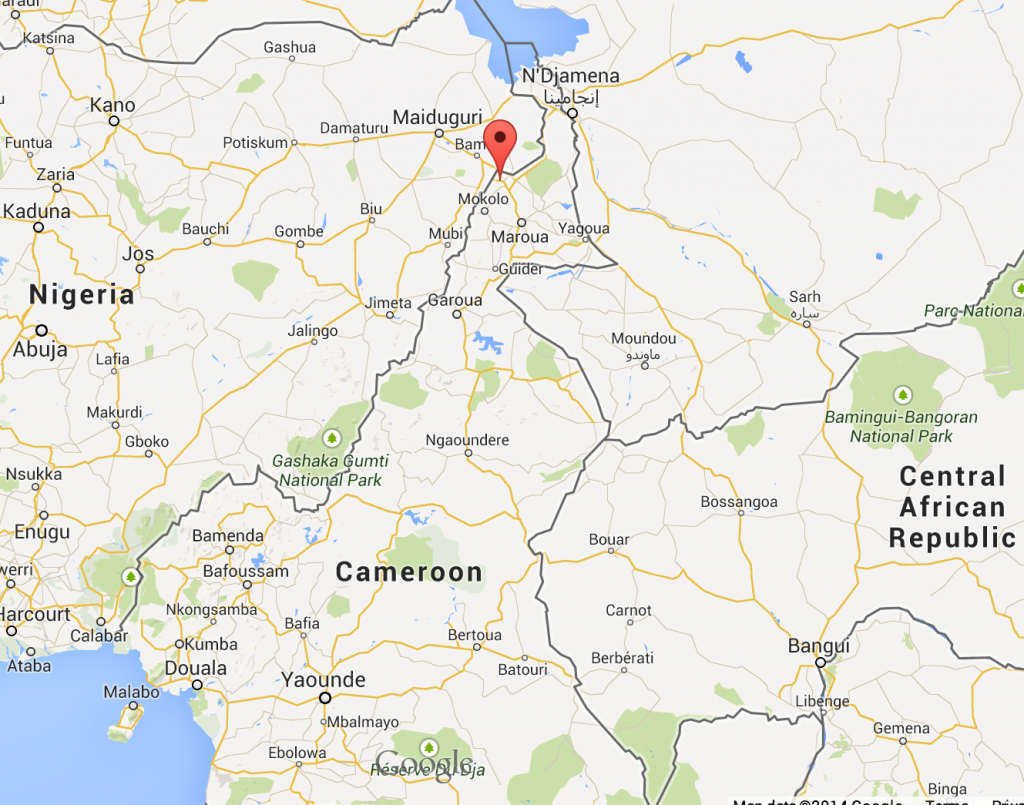
The Obama administration says it expects to deploy about 300 U.S. service members to the African nation of Cameroon to help stop the spread of Boko Haram and other violent extremist groups.
Roughly 90 U.S. service members are already en route to Cameroon to conduct airborne intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance operations in the region.
Background from our prior briefing reports:
Cameroon, which is located next to Nigeria (Boko Haram’s home base) and shares a difficult-to-monitor 300-mile border with it, announced it was going to war with Boko Haram back in May of 2014 when hundreds of Nigerian schoolgirls were kidnapped in a raid. This decision triggered a wave of Boko Haram incursions into Cameroon (including high-profile kidnappings) and retaliatory ground and air operations by the Cameroon Armed Forces.
President Paul Biya next month will celebrate his 33rd anniversary as president (after 7 years as prime minister before that). The Cameroonian military (some parts competent and some parts rickety) could probably use the U.S. military assistance, but there will be concerns as to whether the U.S. is again militarily aiding and training a military force in an autocratic African country after more than a few recent instances of political trouble or repression involving U.S.-trained local military forces.
Cameroon — a country once carved out of colonial remainders by Imperial Germany and then split at random by France and Britain before re-merging itself after independence — now finds itself as an unusually stable dictatorship wedged between the rising conflict in northern Nigeria and the aftermath of the recent genocidal civil war in Central African Republic, exposed along lengthy borders on both sides. The populations in northeast Nigeria and northern Cameroon have long had cultural and economic interchange, since the border was an arbitrary colonial one crossing through an existing society.