Arsenal Bolt: Quick updates on the news stories we’re following.
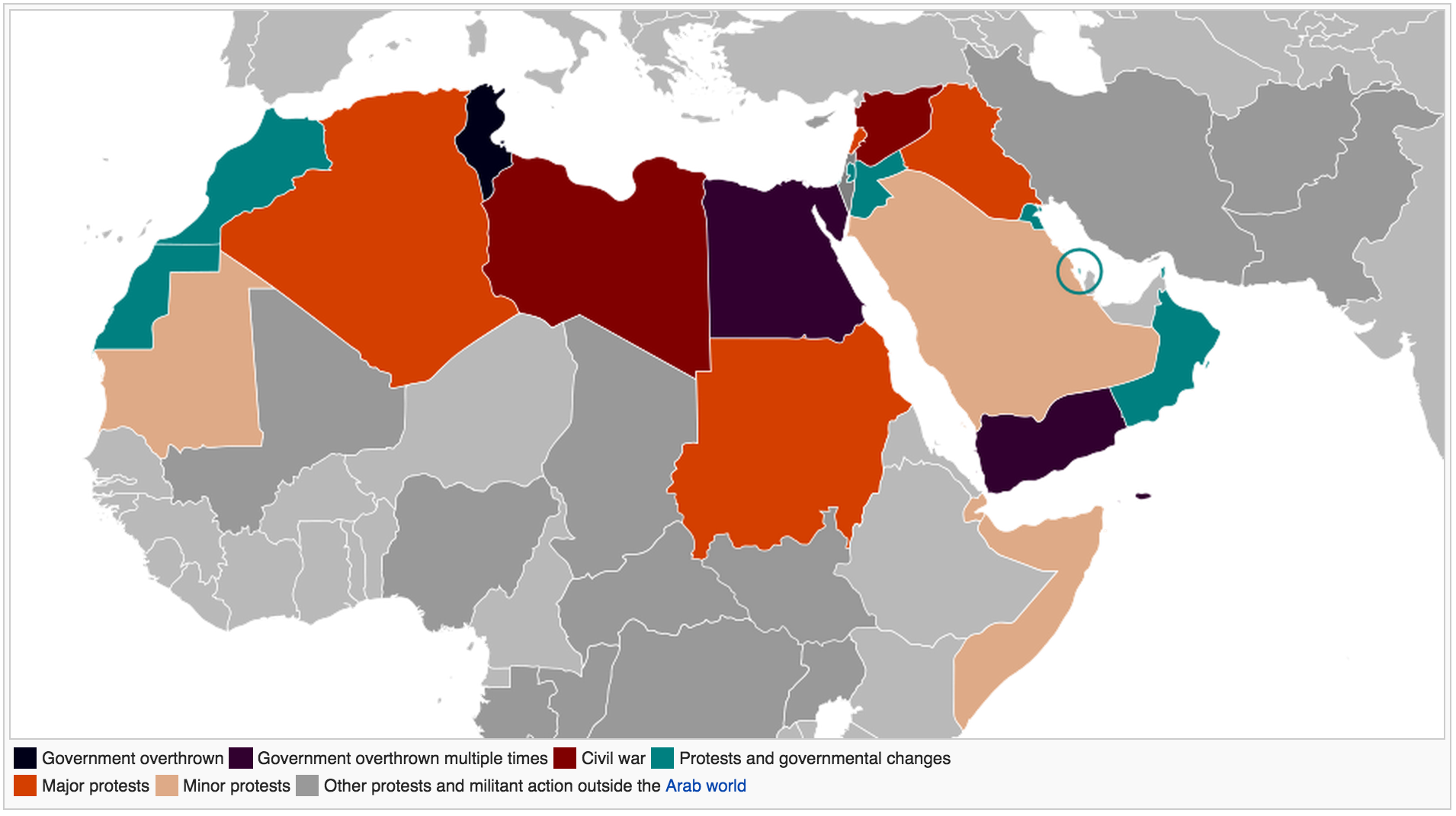
Germany’s Friedrich Naumann Foundation for Freedom – an NGO dedicated to promoting liberalization of governments and markets – recently announced it was closing its longstanding Egypt office, citing unsustainable pressure from the illiberal environment of the current military-backed government. Ronald Meinardus, now directing the South Asia office in New Delhi but formerly directing FNFF’s Egypt office, reflects in The Globalist on his experience watching the revolution die:
Never, on the other hand, will I forget the images of the massacre at Rabaa Al Adawiya where, in a blood bath, Egypt’s military ended all democratic experiments in the Arab world’s biggest nation.
[…]
One of my biggest frustrations was that long time Arab friends and partners would publicly argue that their part of the world was neither ready nor suitable for liberal ideas and practices. Many of these people would support authoritarian rule, arguing it was by far better than giving space to the Islamists, whom they saw as the biggest threat.
The announcement of the closure of the regional office of the liberal Foundation in Cairo coincides with the fifth anniversary of what used to be termed Egypt’s Revolution of January 25.
[…]
Future chroniclers without ideological blinders will note that Egyptians enjoyed most freedoms under the brief rule of the Muslim Brothers who, not by chance, won every single democratic election they were allowed to participate in.





 Egypt’s military-supported “secularist” government under former General Sisi picked a new Justice Minister
Egypt’s military-supported “secularist” government under former General Sisi picked a new Justice Minister 