Not only is riot suppression an increasingly lucrative global business opportunity, but governments in advanced democracies have been taking cues from their more authoritarian brethren in outlawing or severely curtailing the right to peaceful assembly altogether.
In other words, these democracies are demanding non-violent protest, but then outlawing peaceful protest, too. Some recent examples, among many, of this trend:
Under the [Spanish] provision, which goes into effect on July 1, police will have the discretionary ability to hand out fines up to $650,000 to “unauthorized” demonstrators who protest near a transport hub or nuclear power plant. They will be allowed to issue fines of up to $30,000 for taking pictures of police during protest, failing to show police ID, or just gathering in an unauthorized way near government buildings.
[…]
And the United States is hardly doing better. In Baltimore, many of those who protested Freddie Gray’s death were held without charges for over 48 hours. Cells designed for one or two people were crammed with dozens, and prisoners haven’t been allowed phone calls, blankets, pillows, or any contact with lawyers or anyone from the outside world. In 2012, H.R. 347 made protesting near government buildings, political conventions or global summits — except in heavily policed and encaged “free speech zones” — a federal crime. After the Black Lives Matter movement had subsided in New York City Police Commissioner William Bratton demanded a new force of 1,000 police, armed with machine guns, specifically to monitor protests and sought to turn resisting arrest into a felony charge.
This is, of course, antithetical to representative democracy and core founding values of the United States, but it’s also fairly stupid in the long run. Why? Because if there’s one thing humans like almost as much as actually getting their grievances fixed is the having opportunity to loudly tell everyone about their grievances in a public place and to get other people to listen, even if they don’t agree or don’t do anything in response. I’m serious. People will often settle for at least “being heard” if they can’t actually get their way. It’s a lesser form of catharsis and has a positive effect on society in terms of defusing (or diffusing) some of the tensions into more constructive paths before they can build into violence. It’s also vital to incorporating minority political opinions in a theoretically majoritarian system without provoking open conflict.
Unfortunately, letting frustrated people be heard doesn’t seem to be on the agenda anymore in the developed world, democratic or otherwise. To quote the previous item again, an op-ed by Willie Osterweil:
These new laws suggest that the ruling elites are preparing themselves for protracted conflict. Rather than genuflect before the idols of democratic freedoms — or, God forbid, actually attempt to alleviate such widespread social problems as inequality, racist violence and ecological collapse — governments are giving themselves new weapons to crush those who demand change. But once non-violent marches are punished just as harshly as rioting, will protesters stick to passive demonstration? Or will they take the streets with more radical ideas about what’s required to win justice?
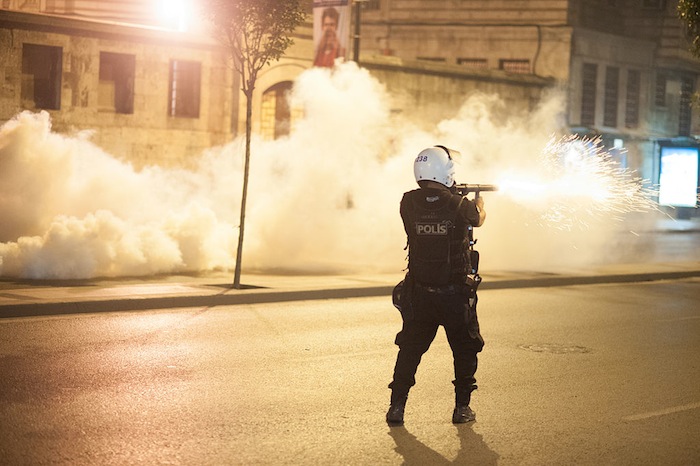

Riot police in action during Gezi park protests in Istanbul, June 16, 2013. (Credit: Mstyslav Chernov via Wikimedia)
Previously from AFD:
“After Baltimore: In defense of riots” by De Ana
“After Ferguson: In defense of non-peaceful resistance” by Bill
“Non-violence has cost at least 2.7 million Black US lives” by Bill