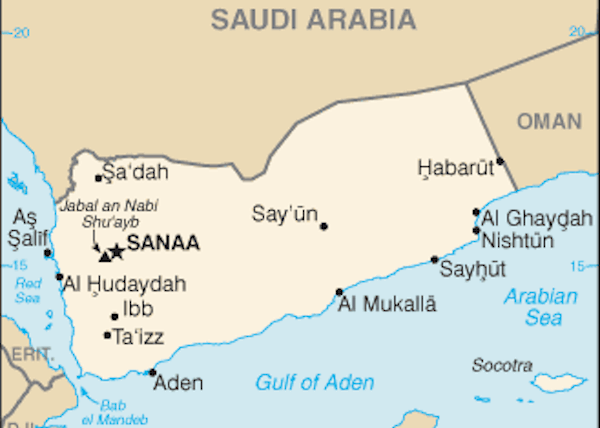
After years of slowly building chaos, The Houthi force is moving against Aden, the government-in-the-south has fled the country, and — as of tonight — the Royal Saudi Air Force has launched an operation into Yemen under the GCC (or possibly the Arab League) at the request of the fallen government.

Flag of Yemen
10 countries are participating in the operation already: Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, Jordan, Egypt, Pakistan, Qatar, Bahrain, Kuwait, Morocco, and Sudan are all said to be participating, with logistical and intelligence support from the United States.
The involvements of Egypt, Pakistan, Morocco, and Sudan are very unexpected and indicate a much wider operation than anticipated. It also strongly suggests that Saudi Arabia was leaning heavily on every government in the Middle East, North Africa, East Africa, and South Asia to whom it has given a lot of money previously. Saudi Arabia is cashing in every favor for a blistering war against the quasi-Shia Houthi rebels in Yemen, unlike with the rather lackadaisical coalition to support the United States against ISIS in Syria. Qatar, which sent no jets at all in the Syria campaign, sent 10 tonight.
Bahrain, which only participated minimally on the first day of the Syria raids, also sent 15 jets. Bahrain’s Sunni monarchy also “owes” Saudi Arabia for brutally suppressing their own Shia uprising in 2011 (during the Arab Spring) with GCC shock troops.
The UAE and Jordan also sent plenty of bombers over Yemen in the initial hours, in a marked contrast from their wavering in the Syria campaign.
This massive undertaking should, in my opinion, also be taken as a clear signal that Saudi Arabia firmly prioritizes the “threat” from Iran and Iranian proxies (which include the Houthis in Yemen but also 100,000 anti-ISIS fighters across Iraq and Hezbollah anti-ISIS units in western Syria) well above the threat from ISIS, despite tough talk on the latter some months ago.
Meanwhile, Iran has countless military advisers and trainers on the ground assisting the huge Iraqi campaign to re-take Tikrit from ISIS, has been providing close-air support and bombers against ISIS all over the Iraqi skies, and reportedly may even have 30,000 regular troops fighting in Iraq directly.
If I’m looking at the facts and figures, Saudi Arabia and the Arab League in general — the purported American allies — are doing far less to combat ISIS than Iran, even if you buy the theory that Iran’s support for Assad accidentally helped create ISIS in the first place.
This war in Yemen against the Houthis, which Saudi Arabia has been stirring up violently for years, seems essentially to be more of an indirect war between Saudi Arabia and Iran.
And this doesn’t even begin to touch the actual al Qaeda presence in Yemen.