This essay originally appeared in The Globalist.

January 2013: French troops being airlifted to Mali. (U.S. Air Force photo by Staff Sgt. Nathanael Callon)
Nothing can ever justify or excuse an act of terrorism against civilians. But that does not absolve us from truly comprehending the links between the foreign and military policy approaches pursued by Western governments and the reactions this generates.
The aftermath of a terrorist attack is an especially difficult time to ask difficult questions about strategy. But just as the United States has faced a lot of (justified) criticism for refusing to acknowledge the direct linkages between misguided interventions and blowback incidents, we cannot apply a different yardstick to France.
Watch for the warmongers
This is all the more critical as, in the wake of the events in Paris, there are those pundits and policymakers who are trying to let slip the dogs of war or beat the drums by defining the scourge of “radical Islam” and “homegrown terrorism” as the root of all evil.
If we should have learned one thing by now, it is that tough talk is not the same as serious, strategic policymaking. It is irresponsible to undertake foreign policies without accurately representing to the public the likely risks to them that it will create.
As we assess the future approach, we must also take account of the role that Western governments have played in creating this catastrophe.
This applies especially to all those who glibly claim that ISIS “cannot be contained; it must be defeated,” as Hillary Clinton has just done.
Such an argument conveniently overlooks the fact that it was the U.S. government that inadvertently gave rise to this movement. Its decades of invasions and unpopular interference in the region ultimately culminated in the Pandora’s box war of choice in Iraq. Out of, and in reaction to, these policies grew al Qaeda and ISIS.
The advocates of such a strategy must also explain what can possibly be accomplished by responding with yet more force in an already war-torn region.
An eye for an eye strategy, while sounding principled, makes the whole world blind to the pitfalls such an approach has been triggering.
The French example
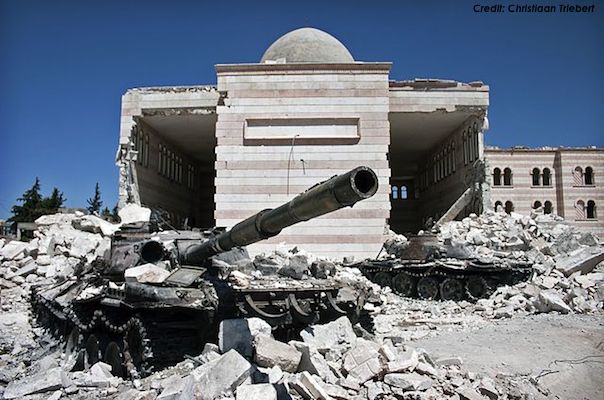
France can actually serve as Exhibit A of the pitfalls of a more “muscular” approach. The cruel attacks in Paris are demonstrably reactive in nature.
The unfortunate reality no one wants to discuss at the moment is that France’s Presidents Nicolas Sarkozy (2007-2012) and François Hollande (2012-present) have pushed the envelope for modern France on maintaining a highly aggressive and forcible military presence in majority Muslim countries.
Not since perhaps the Algerian War has France meddled with, sent troops to or bombed so many predominantly Muslim regions in such a short span.
President Sarkozy led regime change in Libya by air campaign in 2011 at the nadir of his domestic popularity. We know what that resulted in. He did it for oil and whatever it was that Iraq War apologist Bernard-Henry Lévy promised him would transpire.
But his successor, President Hollande, went way, way farther — claiming, almost George W. Bush style, that he was fighting ‘them’ over there to protect France from terrorist attacks at home. This approach painted a much bigger target on France’s back.
Hollande’s misadventures
The Hollande record is this: First, he invaded Mali in January 2013, after it collapsed as part of fallout from the Libya meltdown. He did so purportedly to stop terrorism and prevent the creation of a terrorism launching pad near Europe (despite Libya being much closer and truly festering).
In December 2013, he then invaded Central African Republic to ‘save’ Christians from Muslim militias that had already been disbanded. (It did not help that French troops now implicated in widespread child abuse stood by as Christian militias mutilated Muslim civilians’ corpses in front of them.)
In May 2014, Hollande announced a large, permanent rapid strike force deployment to five “Sahel-Sahara” West African nations, all of which were majority or plurality Muslim. He sent jets to bomb Iraq in September 2014. Finally, a year later in September 2015 he sent jets to bomb Syria.
It is difficult to understand Hollande’s declaration that the November 2015 Paris attacks are an “act of war” by ISIS, in view of the reality that France has already been at war with ISIS for more than a year.
Note, too, that the United States was barely involved in half of those misguided efforts.
Whether or not it can match U.S. capacity, France is no longer a junior partner or even hapless “sidekick” to the United States’ mayhem. In that sense, Hollande has gone much further than Tony Blair ever did during the Iraq War episode. Blair restrained himself to just being a sidekick.
France under Hollande has turned itself into an active cyclone by pursuing a militarized foreign policy – a strategy that may prove self-defeating. Read more