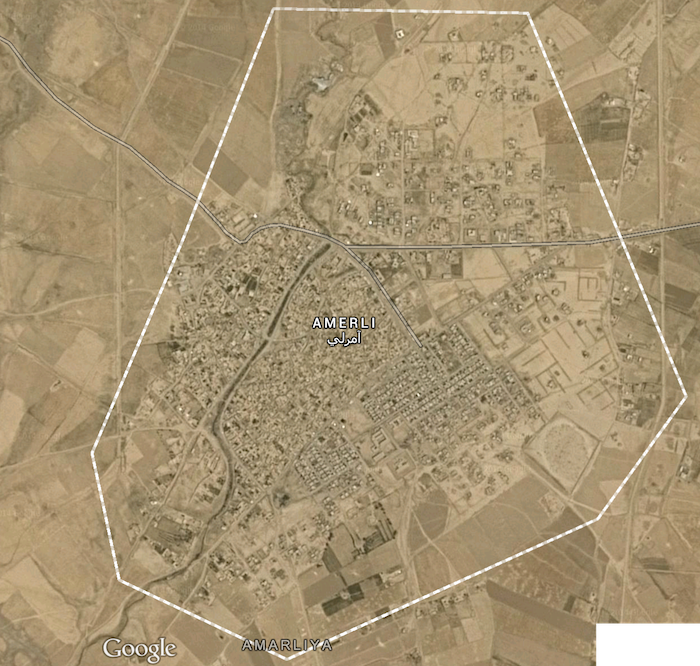
The United States is flailing rapidly toward an ill-conceived military intervention in Syria against ISIS, as I predicted last week, apparently under the inertia of the cop-out analysis known as “there are no good options.” This troubling declaration is a common hand-wave used in Washington to justify stumbling into catastrophic decisions without much of a rational or clear-headed decision-making process, before or after it happens, to silence public criticism.
I really dislike the whole “there are no good options” school of foreign policy punditry and officialdom, because even when there are a lot of bad options and no good ones, that doesn’t mean you should immediately pull the lever on the more horrendous end of the spectrum.
And a spectrum of bad ideas is exactly what we’re looking at here. Doing nothing in Syria continues to be on the less bad end of the spectrum, as I explained at length in last week’s analysis (and in many prior posts). Simply put: Airstrikes in Syria opens a door we are not prepared to walk through, but if this starts, we may well be dragged. Any direct U.S. military intervention in Syria should be avoided, to prevent that.
Additionally, as I examined in a recap of the Wall Street Journal’s investigation of the Assad-ISIS relationship, the Syrian regime has carefully positioned ISIS (and itself) over the course of a year such that the United States may be forced to align with Bashar al-Assad, if it intervenes, at the cost global humiliation and anger of many allies and the Washington Beltway. Already, even just with the start of unauthorized U.S. surveillance flights over Syria, the trolling has begun.
Syria on Monday signaled its readiness to work with the United States in a coordinated campaign against ISIS. But it warned the White House that it needed to coordinate airstrikes with the Assad government or it would view them as a breach of its sovereignty and an “act of aggression.”
Let’s look, too, at an article, by Peter Beinart at The Atlantic, entitled “The Problem With Bombing ISIS.” I have a lot of problems with this article’s framing, but the core premise is correct, in my opinion. A crucial deciding factor of when to intervene in a situation needs to be who fills the vacuum after a U.S. military intervention (if successful!) and whether they are better than the dislodged power, for the people ostensibly being helped:
From Somalia to Kosovo to Libya, the problem with America’s humanitarian interventions has never been ascertaining the nastiness of the people we’re fighting against. It’s been ascertaining the efficacy and decency of the people we’re fighting for. That’s a particular challenge in the case of ISIS in Syria.
In Syria, that’s either going to be Assad or other jihadists in al Qaeda’s Nusra Front or in the so-called “Free Syrian Army” (if they somehow bounce back from the brink of defeat): Read more