The Obama Administration is apparently determined to prevent the fall of Erbil, Kurdistan Region’s capital, at all costs (or at the very least whatever it takes short of ground troops — though that might be on the table, too, as discussed below). It’s one of the advantages of being a longstanding protectorate and ally of the United States. The President ordered airstrikes on ISIS missile launchers and mortars as soon as Erbil came under long-range attack because most of the U.S. presence in Iraq (outside Baghdad itself) is located there and locals were already evacuating in a panic. The concern was that mass evacuation left Americans at the Erbil consulate and other sites even more vulnerable.
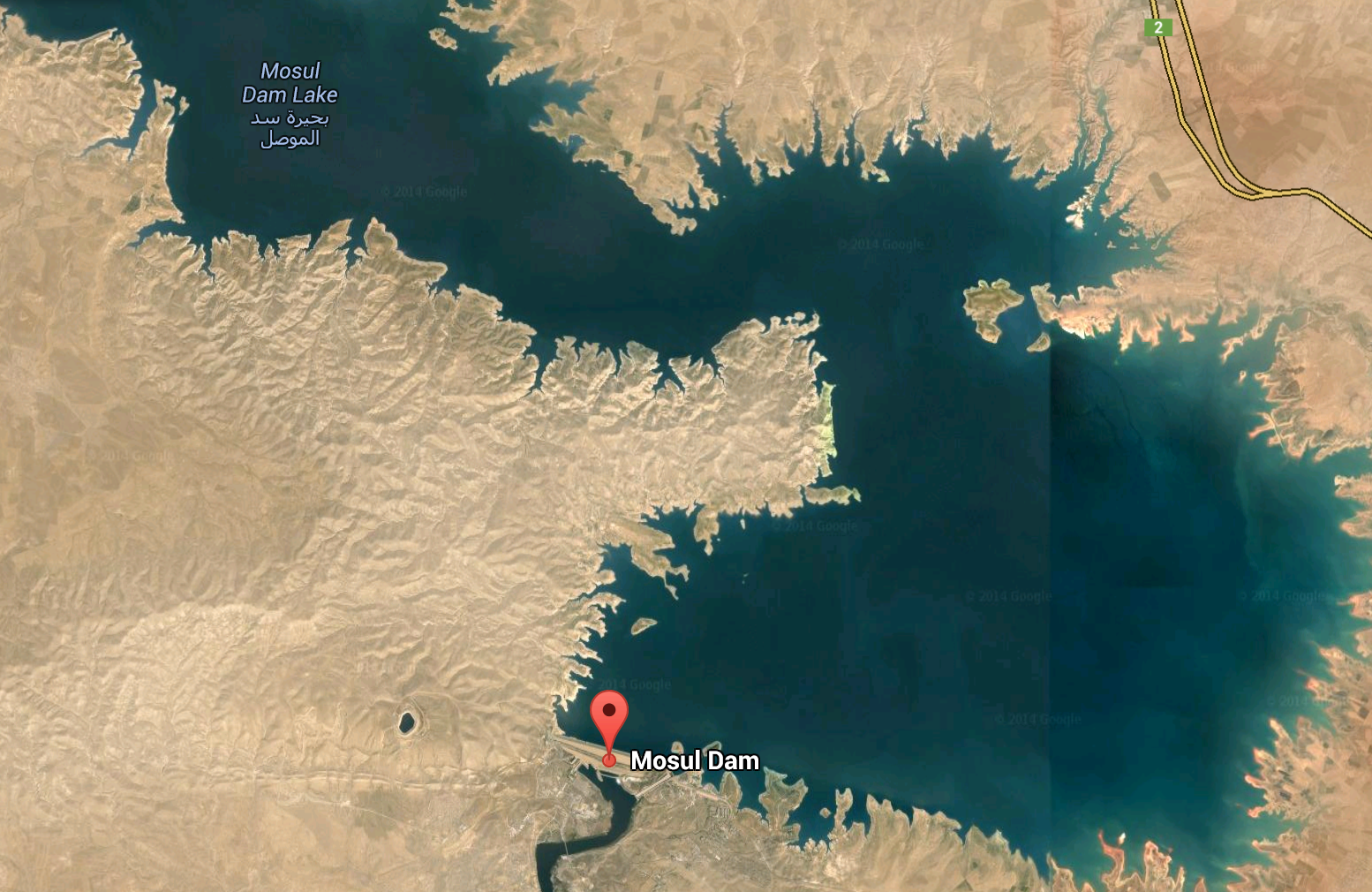
The U.S. military also asserts that the ISIS capture of Mosul Dam poses a risk to the U.S. Embassy in Baghdad, so I suspect it’s within the realm of possibility that we may see U.S. Special Forces land to re-take it very soon. Presumably this would be a very limited action to eject ISIS troops from the dam facilities and (one hopes) set up more secure defenses to help local paramilitaries and the Iraqi security forces hold it against future attacks. The destruction of this Tigris river dam, as attempted unsuccessfully by Saddam Hussein in 2003, would likely release quasi-apocalyptic flood conditions on the rest of Iraq to the south. That, however, would require ISIS to make the calculation that destroying the city of Mosul and much of their own territory in the process was worth the destructive power further south. It seems more probable they will use the dam, which is the country’s largest hydroelectric dam, to cut off water and power to the south. A 65-foot tall wall of water smashing through Mosul, the most important city in ISIS hands, seems a bit too Hollywood. Thus, it might not make much sense for the U.S. military to try to re-take the dam.
On the other northern front, Syrian Kurdish forces say they have broken out 10% of the Yazidis trapped on Mount Sinjar, which is located near the Iraq-Syria border. They will be taken across into an anti-ISIS rebel-held area of Syrian Kurdistan.
The mountain, which is perhaps better described as a 25-mile-long and 10-mile-wide ridge, is a dozen or so miles from the Syrian border.

USGS Satellite Image of Mount Sinjar ridge. Dark, bent line in the upper left corner is the Syrian border.
It’s a very distressing situation. Before any evacuations, 40-50,000 people were trapped on a mountain without food or water, completely surrounded by ISIS forces. The latter are reported slowly starting to move in and are snatching women and girls. U.S. and Kurdish relief aircraft are continuing to drop food, water, and other supplies on to the mountain — reportedly under enemy fire.
Meanwhile, the Kurdistan Region has had to absorb 200,000 internally displaced Iraqis since Monday alone. On top of that, tens of thousands of local residents started moving southward within the region on Thursday in an effort to evacuate before ISIS invades.