The northern Syrian border town of Kobani and surrounding villages — predominantly Kurdish — recently came under siege by ISIS tanks and artillery, as discussed previously on this site. This collapsing Kurdish enclave quickly turned into a mass exodus of at least 150,000 Syrian Kurdish civilians in a matter of days, as Turkey warily opened its border to avoid total pandemonium (and the possibility of a massacre happening so close to the border that it would probably appear on Turkish evening television news).
As U.S. airstrikes in Syria had not yet started but were increasingly seeming inevitable, I suggested that this ISIS armored unit closing in on Kobani and its relatively pro-American Kurdish population was probably going to be an early target:
Depending perhaps on Turkey’s views on the potential future threat posed by the now-beleaguered YPK [Syrian Kurd] fighters and the Kurdish villagers they are trying to protect, as well as whether the influential Iraqi Kurdish leadership is concerned about the situation — both of which have a significant voice in setting American military priorities in the region and are much friendlier to Syrian Kurds after months of ISIS advances into Iraq — ISIS tank units attacking Kurdish areas in northern, central Syria seem like a pretty tempting target for American-led coalition airstrikes on ISIS forces in Syria, once those begin in the coming weeks.
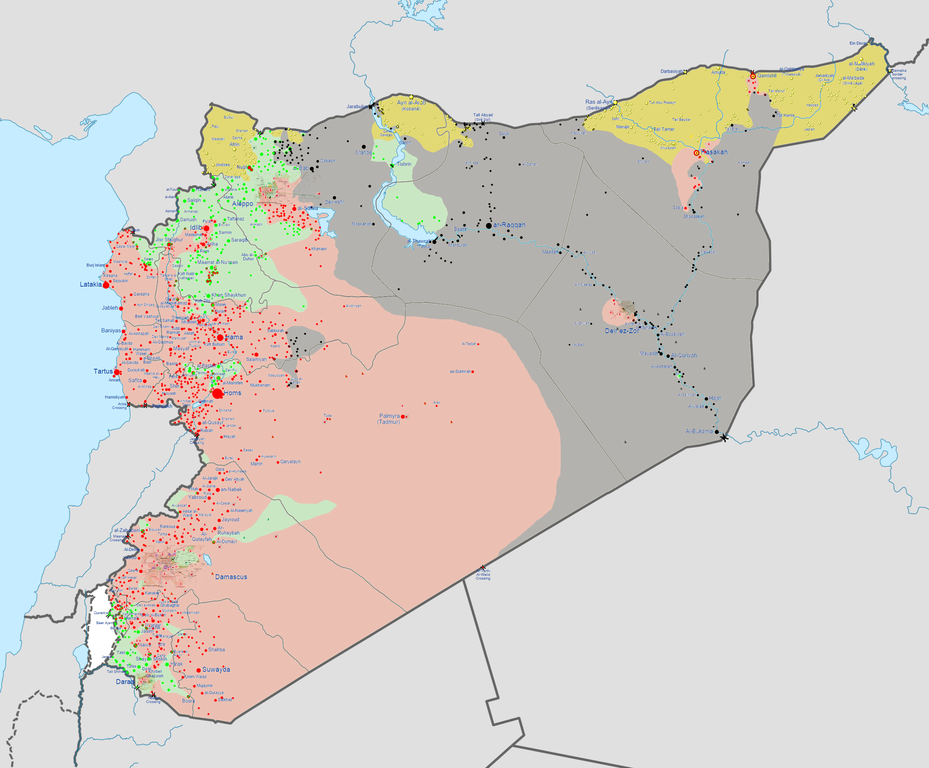
US-led coalition airstrikes began in Syria this past Tuesday, primarily focusing on military and administrative targets in Raqqa, the so-called ISIS “capital,” to the south (see map below). But on Saturday — day six of coalition strikes in Syria — the first sortie to relieve Kobani and the besieged Syrian Kurds was initiated.
According to the New York Times reporters on scene just across the border in Turkey, this first action appeared to have only a small effect, apart from slightly slowing the pace of ISIS shrinking its perimeter in the half-circle it had established around the town and up to the border; ISIS artillery still reached range to hit the town itself for the first time later on Saturday:
The Pentagon said on Saturday that it had conducted its first strikes against Islamic State targets in a besieged Kurdish area of Syria along the Turkish border, destroying two armored vehicles in an area that has been the subject of a weeklong onslaught by the Islamic State.
[…]
After days of pleading for air cover, Kurds watching the fighting from across the Turkish border west of Kobani were gleeful as jets roared overhead and two columns of smoke could be seen from the eastern front miles away. They hoped it meant that American warplanes had finally come to their aid.
[…]
Nearby, Syrian and Turkish Kurds cheered from hilltops dotted with fig and olive trees and army foxholes as Kurdish fighters scaled a ridge and fired a heavy machine gun mounted on a pickup truck at an Islamic State position less than a mile from them. Islamic State fighters could be seen moving from a nearby village, but seemed to be shifting tactics in a hedge against airstrikes, moving one vehicle at a time rather than in a convoy.
The fighting took place just a few hundred yards inside Syria, clearly visible from hilltop olive groves in Karaca, a frontier village on the Turkish side of the border. They fought with rocket-propelled grenades and heavy machine guns west of Kobani, the central town in the region.
[…]
On the eastern front, a Kurdish activist, Mustafa Ebdi, said from Kobani that an Islamic State command post, a tank and a cannon had been hit by the American strike. Still, hours later, Islamic State shelling hit Kobani’s main town for the first time, killing at least two people.
In a statement, the United States Central Command said that strikes around the country had been carried out with forces from Saudi Arabia, Jordan and the United Arab Emirates — it did not specify which aircraft hit which areas — and that “all aircraft exited the strike areas safely.”
We can probably expect more coalition airstrikes in the coming days, if the situation is not too fluid to hit from the air. The fact that ISIS positions are now visible from across the border may also make it easier to get accurate enough intelligence to target the attacks.
There is also extensive discussion — following heavy lobbying by the Obama Administration this past week — that Turkey may be about to join or support the military coalition directly attacking ISIS within Syria’s borders. This would at least involve providing air bases, if not bombers, or possibly even ground troops tasked with establishing a hypothetical refugee safe zone on the Syrian side of the border with Turkey.
The latter, far more expansive and ambitious option — which should raise a lot of questions and red flags all around — is probably less likely than some level of supporting the air operations. Those operations would probably become significantly safer for coalition pilots by dramatically shortening the flight distances required over hostile territory and Syrian air defenses.
[Our update for September 30, 2014: “ISIS still moving faster than coalition forces on Kobani; will Turkey enter?”]
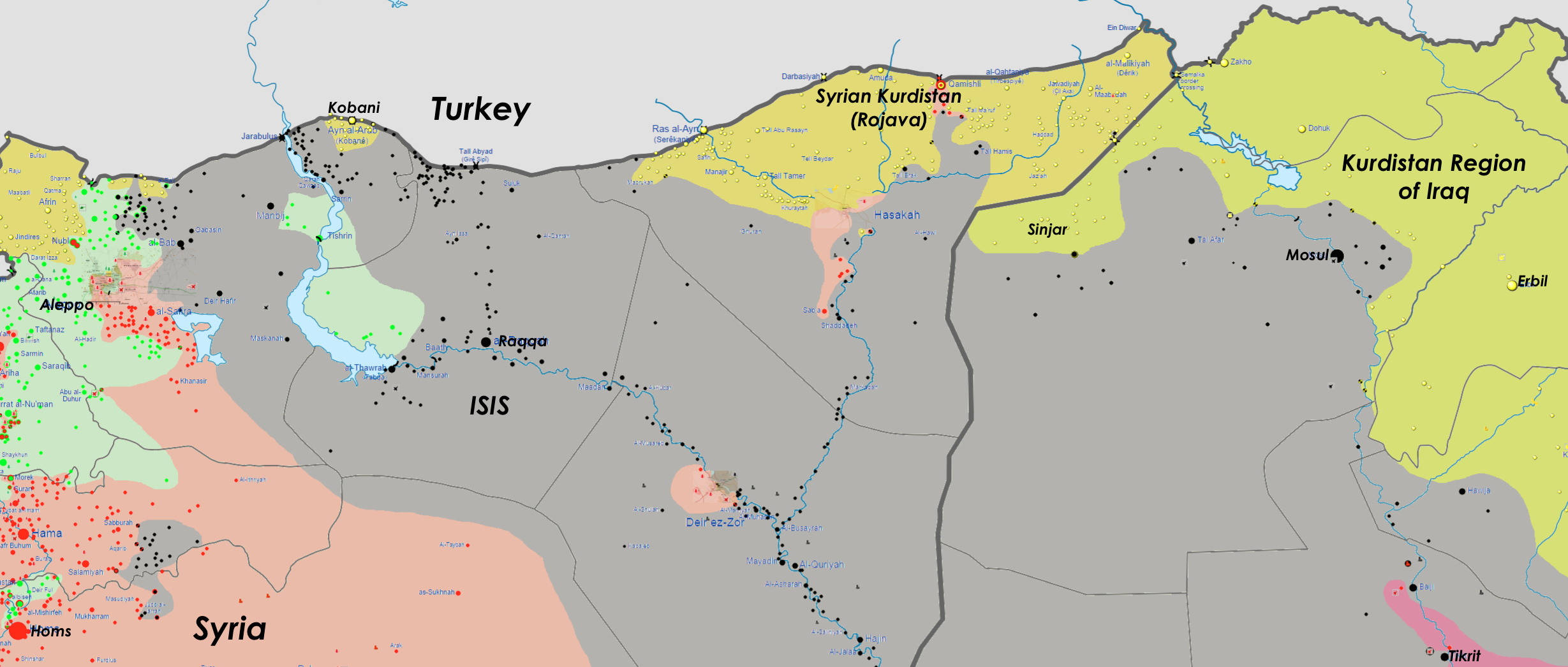
Click to enlarge: Detailed conflict map of Northern Syria and Northern Iraq, September 26, 2014, including Kobani / Ayn al-Arab. (Adapted from Wikimedia)