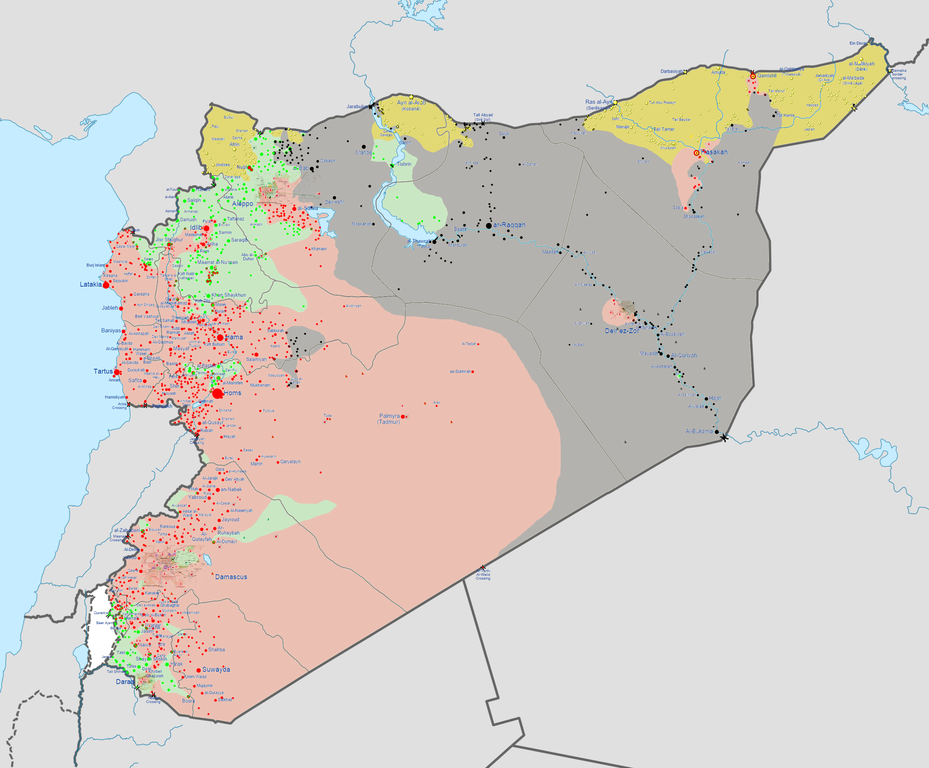
The BBC published a huge, multi-angle international law analysis by Marc Weller, Professor of International Law at University of Cambridge, on whether and to what extent the US-led operations against ISIS are legal under international law without United Nations approval. It’s a very well-balanced examination, with various arguments raised both ways for each specific element (such as operations inside Syria versus inside Iraq, or the legitimacy/sovereignty questions surrounding the governments of both Syria and Iraq).
Below is an excerpt specifically regarding the legal case for narrow military operations against ISIS, within Syria, without UN approval, on behalf of Iraq — the position that I find most plausible if any case can be made at all:
According to a ruling of the International Court of Justice in the 1986 Nicaragua case, where the US was found guilty of violating international law by supporting armed Contra rebels, self-defence could only be invoked by Iraq against Syria if IS acts as a direct agent of Damascus and under its operational control.
This is not the case. Instead, the Syrian government has lost all control over the parts of Syria held by IS.
Indeed, until very recently, it has made no attempt to dislodge it, leaving this task instead to the armed opposition groups. Damascus is manifestly unable or unwilling to discharge its obligation to prevent IS operations against Iraq from its own soil. Syria cannot impose the costs of its inaction or incapacity in relation to IS on neighbouring Iraq.
Hence, under the doctrine of self-defence, the zone of operations of the campaign to defeat IS in Iraq can be extended to cover portions of Syria beyond the control of the Syrian government.
[…] short of forming an unsavoury alliance with the Assad government, the strongest legal basis for action against IS in Syria is ancillary to the campaign now being conducted in Iraq. This may also extend to other affected states, such as Jordan. The theatre of operations may extend to parts of Syria as may be strictly necessary to conclude that campaign successfully.
If they want to shake off the comparison to George W. Bush’s 2003 invasion of Iraq and want to make this Syrian operation have a veneer of legality, the Obama Administration should say over and over again something along these lines:
We have been requested by the sovereign government of Iraq to halt and destroy a non-state combatant force attacking them from across the Syrian border. The government of Syria has not only failed to prevent the establishment of and cross-border attacks by this non-state actor, but they have actively allowed them to flourish within their own borders. Therefore, we are acting to halt attacks against Iraq from inside Syria, on behalf of the government of Iraq, which lacks the capacity to defend itself from the origin point of these attacks, located within its neighbor’s territory.
I’ve made clear on this blog that I think this operation in Syria is deeply misguided and a big mistake, but I figured I’d at least look into the possible case for why this is legal, since even that has been unclear to me. The above is the best I’ve been able to piece together so far.

File photo of the United Nations Security Council.