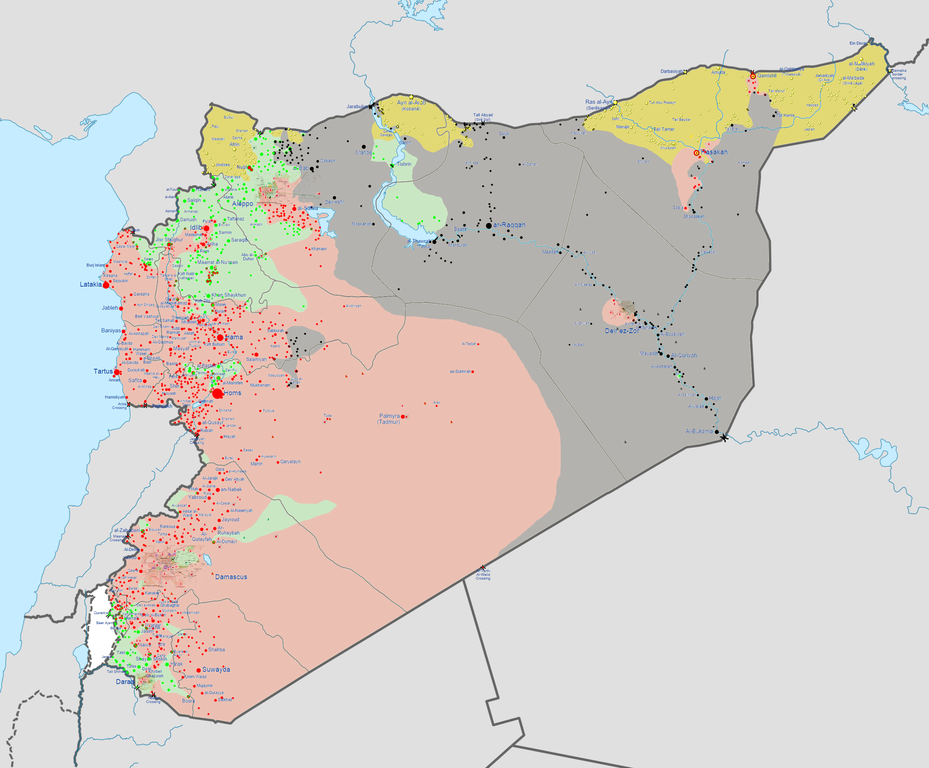
15 years after a US-led NATO bombing campaign freed the predominantly Muslim province of Kosovo from Serbia, youth unemployment stands at 70%. Now more than a hundred young residents, from a country with a huge statue of Bill Clinton in the capital (photo below), have gone off to join anti-American terrorist groups in Syria and Iraq.
Balkan fighters have participated in Islamist insurgencies elsewhere in the past, but more often against Russia — which, unlike the US, supported Serbia against its Muslim neighbors in the former Yugoslavia. This time, would-be combatants from places like Kosovo are joining ISIS, a group that has moved beyond attacking places in Syria and is now staging suicide attacks in Iraq’s capital against the US-supported government — using at least one Kosovar recruit so far — and has called for attacks on U.S. and British citizens everywhere.
The talk and stories of people disappearing to the Syrian conflict from Kosovo, a country of 1.8 million people, now abound. This is especially true after Kosovar fighters began propagandizing from Syria to folks back home over social media. Even some former NATO assets have reportedly joined up to become jihadists in Syria. In another case, a man kidnapped his 8-year-old son away from his wife and went to Syria with him. Senior religious officials in Kosovo have been arrested for allegedly preaching recruitment on behalf of extremist religious groups in Syria, including ISIS.
The general population disapproves very strongly of the one or two hundred citizens who have gone to join extremist groups in Syria. But Kosovo has no jobs for the vast majority of young men. In contrast, ISIS can offer excitement and a sense of purpose, along with food provisions and payroll funds from the millions of dollars added daily to its cash reserves. And the situation is not unique. Nearby Bosnia, which also has been experiencing very high unemployment and has an even more extensive prior history of contributing recruits to Islamic extremist insurgencies all over, has seen some of its citizens be similarly lured to the civil war in Syria.
The lessons, as always, are that you can’t fix every problem with airstrikes and you can’t fight extremism without fighting poverty and joblessness. A multi-million dollar Western grant for jobs training and creation in the Balkans wouldn’t go amiss right now. Too bad they’re cutting such programs in their own countries already.
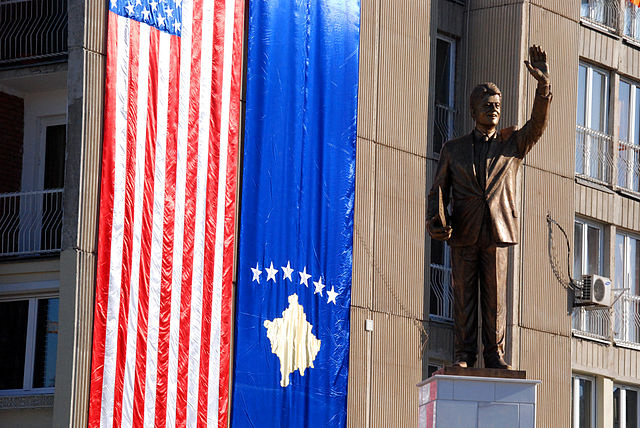

Statue of Bill Clinton in Pristina, Kosovo, November 2009. (Credit: Arian Selmani via Wikimedia)