The talk of Europe in the past week has been the snap elections called for Greece at the end of January, which may bring to power a new leftist party called Syriza, which seeks to make domestic reforms and EU reforms that will help average working people and end widespread corruption. Critics have called it “populist” or “radical,” but everything I’ve seen indicates it’s not particularly radical in reality:
Syriza’s manifesto proposes that repayment of debt could come through economic growth, rather than from budget cuts. It wants a European new deal backed up by an investment bank; an all-out war against the tax avoidance endemic in Greek society; an emergency employment programme; a raised minimum wage; and the restoration of collective bargaining.
More:
Syriza promises first to achieve a substantial write-off of Greek debt and, second, to lift austerity by aiming for balanced budgets, instead of the surpluses demanded by the troika. It will reconnect families to the electricity network, provide food relief and shelter the homeless. It will take immediate action to reduce unemployment through public programmes. It is committed to lowering the enormous tax burden and to boosting public investment in an effort to accelerate growth.
There is nothing radical, much less revolutionary, in these policies. They represent modest common sense and would open a fresh path for other European countries. After all, Syriza has repeatedly declared its intention to keep the country within the economic and monetary union, and to avoid unilateral actions. There is little doubt that its leaders are committed Europeanists who truly believe that they could help transform the EU from within.
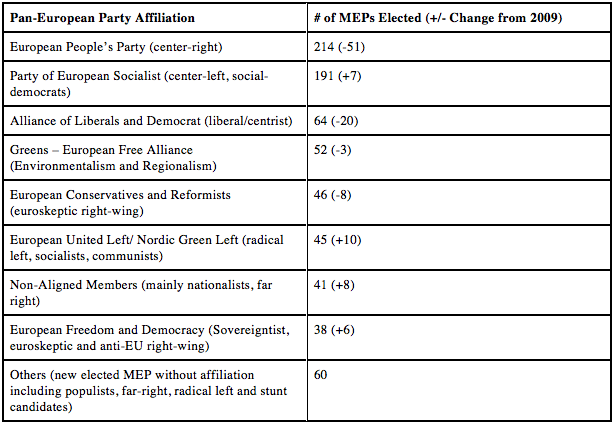
Arsenal For Democracy’s guest post by Etienne Borocco, on the 2014 European Union elections, also drew a strong contrast between Syriza on the populist left and the legitimately frightening populist but ultra-right-wing parties rising across Europe, including in Greece:
Additionally, we should also qualify the right’s surge by noting that the radical left made a sharp increase in Southern Europe and in Ireland. The EUL/NGL gained 10 seats. The Greek party Syriza, whose national leader Alexis Tsipras was the EUL/NGL’s candidate for the European Commission, arrived first in Greece. In Spain and in Portugal, the radical left also earned very good results, via new parties such as Spain’s “Podemos,” which ideologically aligns with parties like Syriza, or via older organizations like the Communist Party of Portugal. The far left collectively won as many seats as the Non-Attached members. Notably, in contrast with the right, leftists like Tsipras are not against euro or the EU as a concept; he only denounced the austerity policies advocated by the EU leaders in recent years.
They are pro-Europe and pro-reform, just not pro-austerity. They are also not neo-Nazis like Golden Dawn, the ultra-right-wing party in Greece that has also been boosted significantly after four years of economic grind on the poor and lower middle class.
In a recent post on his blog, economist Uwe Bott argues that the rise of Syriza in Greece provides an incredible opportunity for Greece to escape the tangle of its debts — like Alexander the Great slicing through the Gordian Knot instead of trying to untie it — and for eurozone-leader Germany to help the country do so in a responsible manner … if it chooses to:
Like many fables or legends there is a moral to this story: Was Alexander the Great cheating when he cut the knot with his sword or was his an act of genius? Or to put the analogy in this context: Would a Greek default be cheating or the only plausible solution to an intractable problem?
Of course, the troika would scream: Fraud! After all, most of the irresponsible lending to Greece has long been transferred from the private banking sector to public accounts at the IMF, the EU Commission and the ECB.
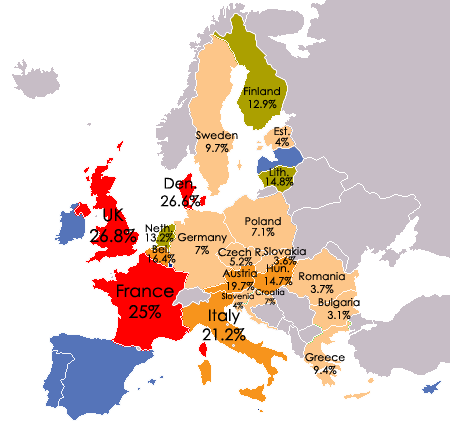
Now, many Greeks would call a default ingenious. After all, Greek GDP has plummeted by 25% during the austerity program. Unemployment stands at 25% with youth unemployment double that. Pensions have been cut in half. Poverty is skyrocketing. Suicide rates have doubled and infant mortality is up as the public healthcare system has collapsed.
So, from a Greek perspective what is not to like about a default? Some of the alleged consequences, such as kicking Greece out of the Eurozone, turn out to be paper tigers. There are no means by which Eurozone countries can actually expel a member. In other words, a Greek default within the Eurozone is possible.
However, defaulting on one’s debt is not to be taken lightly. The default would exclude Greece from access to capital markets important to its private sector and banks.
He also warns in the full post (which I’ve only clipped bits out of) that there is a real risk that an entirely unrestrained default — which Syriza seems to want to avoid anyway, if the EU will help work out a deal — could cause a contagious shock that topples other economies and markets (particularly, he finds Italy a likely candidate). But that’s why Germany needs to lean in and embrace the new movement in Greece, to ensure it has a say in how any default or partial default is managed, so it doesn’t cause panic across Europe: Read more




 Unfortunately, one of the persistent features of Italy specifically has been high debt and low growth.
Unfortunately, one of the persistent features of Italy specifically has been high debt and low growth.