We didn’t record a new episode this week due to the holiday weekend. On WVUD, we will re-air last week’s episode (with a minor cut to remove a numerical error).
Author Archives: Bill Humphrey
Iraq’s army is still comically terrible
(Comic in the cosmic sense. Not for the people affected in Iraq.)
ABC News reports that hundreds of ISIS fighters walked into a city that days earlier had had thousands of Iraqi troops: “Ramadi Fell to ISIS Fighters Even Though They Were ‘Vastly Outnumbered’ by Iraqi Troops”
The pullout of the Iraqi counterterrorism unit from Ramadi first appeared in the Kurdish news agency Rudaw. The departure of that elite unit led other Iraqi military commanders in the city to order the departure of their troops even though they held a significant numerical superiority, the U.S. official said.
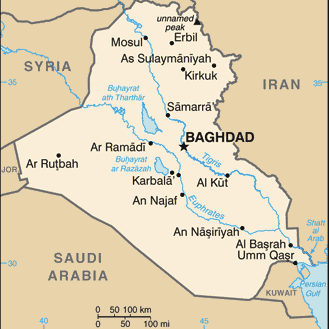
According to the anonymous Kurdish commander interviewed by Rudaw (linked above), the well-armed, American-created Special Ops unit began disappearing from Ramadi in the lead-up to the ISIS takeover. The Office of the Prime Minister of Iraq had not ordered the withdrawal and was not informed of it until the other units began calling it in and asking what was going on.
And in an eerie echo of the fall of Mosul 11 months before:
They pulled out so fast that in most cases they left their vehicles intact with their weapons and ammunition inside. […] By the evening of that day, most of the soldiers of the Special Operations had fled. Even the personal guards of the commander took with them their six Humvees and left the commander alone.
All the other units that remained were vastly less well-equipped to withstand an ISIS assault and felt they had little choice but to retreat hastily.
We torched what we couldn’t carry to prevent it from falling to ISIS. […] At 6pm, I was still inside the city stadium. When I realized it was all lost we pulled out, too. Along the way out of Ramadi I caught up with the force that had withdrawn earlier. There were 600-700 vehicles filled with soldiers, police officers and their families.
Free college AND a better Wall St? Sanders sees a way.
 Senator Bernie Sanders has unveiled his latest policy proposal as part of his Democratic presidential campaign: Free public college, funded via a new financial transactions tax to discourage damaging Wall Street speculation. It’s a step up from his earlier pre-campaign proposal of cutting tuition only in half. Here’s a summary of his new plan:
Senator Bernie Sanders has unveiled his latest policy proposal as part of his Democratic presidential campaign: Free public college, funded via a new financial transactions tax to discourage damaging Wall Street speculation. It’s a step up from his earlier pre-campaign proposal of cutting tuition only in half. Here’s a summary of his new plan:
Annual tuition costs at those institutions add up to roughly $70 billion, according to a fact sheet from Sanders’ office. The proposed legislation would require the federal government to compensate for two-thirds of that sum, with the states making up the additional third.
[…]
The federal funding for Sanders’s proposal would come from a tax on financial transactions. Stock trades, bonds, and derivative trading would be taxed at rates of 0.5 percent, 0.1 percent, and 0.005 percent, respectively. Supporters of the financial transaction tax […] say it is not only a progressive way to raise revenue but would also discourage dangerous levels of Wall Street speculation.
A recent report from economist Joseph Stiglitz and the Roosevelt Institute, intended to provide a comprehensive framework for reworking American economic policy, endorsed a financial transaction tax as a way to “penalize short-term traders and incentivize longer holding periods, thus reducing instability and encouraging longer-term productive investment.”
Unfortunately perhaps the biggest pitfall of this plan — though it is (abstractly) an excellent starting point for a negotiation in Congress — is its dependence on state governments for a third of the funding. Low-cost public colleges and university educations are already being demolished in the name of dogmatic tax cuts. This plan depends on somehow convincing dozens of states not to slash funding / hike tuition and fees for their public colleges. But it’s a lot better than nothing.
Related reading on…
– How much would it cost to make public colleges free?
– Corporate borrowing diverted to shareholders, not investment
– Putting Finance Back in the Box
– Stock market speculation
– Billionaire stock speculation
Lessons from Burundi’s post-Civil War constitution
The following is an installment in my ongoing series on the 2015 Burundian constitutional crisis.

Flag of Burundi
After reading the 2005 French-language Burundian constitution myself, I have tentatively come to the conclusion that the current President, Pierre Nkurunziza, is technically constitutionally allowed to seek another term — but only by deliberately misconstruing some poor word choices in the text. First, I present my textual analysis to develop this finding. Second, are my recommendations on what lessons can be drawn from this crisis, in terms of future drafting of documents to guide political transitions and post-transition foundations.
Basically, there are two conflicting elements in the text. Article 302 stipulated that the first “post-transition” president — which ended up being Mr. Nkurunziza — specifically had to be elected by both chambers of parliament, rather than the voters directly, “on a purely exceptional basis”:
A titre exceptionnel, le premier Président de la République de la période post-transition est élu par l’Assemblée Nationale et le Sénat élus réunis en Congrès, à la majorité des deux tiers des membres.
(My direct translation: “On a purely exceptional basis, the first President of the Republic of the post-transition period is chosen by the elected National Assembly and Senate assembled in Congress, with a two-thirds majority of the members.”)
But at the same time, Article 96 states that (in general, presumably): “The President of the Republic” is to be “elected by direct universal suffrage for a five-year term renewable once”:
Le Président de la République est élu au suffrage universel direct pour un mandat de cinq ans renouvelable une fois.
So President Nkurunziza’s argument is that because he was indirectly elected under Article 302 in 2005 and then elected directly to a five-year term in 2010 that means he is eligible to renew his term one more time by direct election. Which is pretty sketchy — but a literally acceptable interpretation of the text, since Article 96 failed to take the lingering effects of Article 302 (which falls under the “Special Provisions” Title XV) explicitly into account.
Lessons: The wording of Article 96 is grammatically and syntactically stitched together for elegant efficiency rather than explicit clarity, which now seems to have been a mistaken decision. I believe one of the former Burundian Supreme Court members labeled it against the “spirit” of the document and the Arusha Accords that preceded it, even if it was perhaps a textually permitted interpretation.
Of course, there’s little likelihood that preventing this loophole could have avoided the current situation entirely, given that the President was determined to amend the constitution anyway, until he discovered he could use the loophole instead and avoid the hassle. Clearly he had an agenda, with or without this language error. Still, it has needlessly provided him a very convenient shield for his actions. And that, at least, could indeed have been avoided.
Recommendation to future transitional/foundational document drafters: Break up your sentences. And account for deliberate misinterpretations of conflicting provisions. If it had said “The President of the Republic is elected by direct universal suffrage. A presidential term is five years in length and renewable once” there would likely be no way to misread it intentionally. By joining those three thoughts (direct election AND term length AND term limit) into one sentence, it made the term limit contingent upon the election method, which itself had been exceptionally overridden in the other article for the purposes of the first post-transition term only.
While this subject may seem excessively narrow to which to devote a detailed analysis, I bring up these observations about the importance of precise drafting because I found it to be similar to Burkina Faso’s incredibly messy constitutional revisions that (apparently inadvertently!) left literally no one in line to succeed the presidency upon a vacancy, forcing — or at least facilitating and quasi-legitimizing — a military coup when the president resigned unilaterally. These decisions on wording can have far-reaching implications years later.
There will be a next political and economic leap forward
Why should it be surprising that systems and processes created 50-70 years ago no longer work or command broad popular support? An international order created in a cauldron of Cold War and unresolved global colonialism has broken down in a completely different world? You don’t say!
Processes of democracy have remained largely stagnant since a period before internet, computing — or even legal participation by most of humanity. Many of its elements have hardly been modernized in many of the world’s “leading” democracies since before even all adult White men had the right to vote, let alone everyone else.
Many if not most of the major parties or their clear predecessors in the northern industrialized democracies (including those in the United States) were launched/became serious or were significantly reforged a little over 100 years ago. Of those centennial parties, few have undergone serious, radical transformation since then, even after two world wars and the end of the Cold War. They may have moderated or moved toward a midpoint, or they may have consolidated toward the wings, but they are largely still organized along century-old ideological axes.
In the span of 50 years, virtually all the global conditions and realities have changed. Virtually none of the governing, formal organizing, or official economic systems have.
History isn’t “finished” or “completed.” It didn’t end in 1965. It just keeps evolving, constantly. Why would you expect to see fewer radical changes in the global situation in the coming century (or quarter-century) than in the last century (or quarter-century)? If anything, they seem likely to grow more frequent.
Why are there so many people in positions of power or the media who seem stunned and confused that there is widespread public dissatisfaction in stagnant and unresponsive institutions at a national, supranational, and global level when they were devised 50, 70, 100, or more than 200 years ago and have barely been revised since? Why are they writing it all off as the misinformed whining of ignorant masses, after spending decades preaching about the wonders of democracy and public participation in self-governance?
There is no “permanent” order of things unchained from time, place, or circumstance. There’s no “inevitable” course of political and economic development. Why are we collectively so unwilling to begin to consider the next evolution of the two?
Further adventures in Egyptian pseudo-secularism
 Egypt’s military-supported “secularist” government under former General Sisi picked a new Justice Minister after the most recent one put his foot very deep in his mouth. This one promises to be somehow more controversial. Here are just a few quotations from incoming Justice Minister Ahmed el-Zend, out of a veritable cornucopia of outrageousness:
Egypt’s military-supported “secularist” government under former General Sisi picked a new Justice Minister after the most recent one put his foot very deep in his mouth. This one promises to be somehow more controversial. Here are just a few quotations from incoming Justice Minister Ahmed el-Zend, out of a veritable cornucopia of outrageousness:
On a visit to Mecca, he previously gave an interview calling for the full imposition of Sharia law in Egypt – rather than it being acknowledged constitutionally as the “principal source for legislation” as at present.
He specifically called for that to include penalties of “hudud” – corporal penalties for moral crimes such as beheading for apostasy, lashing for fornication, and amputations of limbs for theft.
“We have in our penal code some articles that contradict Islamic Sharia,” he said. “I would like the penal code to become Islamic from A to Z.
“I would like a single article to be added to the penal code – that Islamic Sharia to be applied with hudud.” As critics noted, even the Brotherhood never calling for immediate application of hudud – a practice followed only in the most authoritarian Muslim countries such as Saudi Arabia and Iran, and abandoned elsewhere.
I still can’t believe all the Western suckers and Islamophobes who fervently believed the military coup in July 2013 would end religiously-influenced government in Egypt. In reality, as I’ve said many times, the military just wanted military-led ultraconservative Islam, not liberal secularism.
By contrast, the supposedly dictatorial administration led by Muslim Brotherhood officials wanted plural, moderate Islamic democracy. In many ways, the Brotherhood’s version of political Islam was demonstrably far less hardline than that of the military’s — and it was perhaps even less conservative than Egyptian society as a whole. This is just another piece of evidence on the mountain already plainly visible: The secularists got duped in their own haste to eject the Muslim Brotherhood.
In Ethiopia, US State Dept. has baffling view on democracy
According to the U.S. State Department, Ethiopia is a violently totalitarian single-party state. Also according to the U.S. State Department, Ethiopia is a great democracy.
For example, during a recent visit to Ethiopia, Undersecretary of State for Political Affairs Wendy Sherman praised Ethiopia as a vibrant and progressive democracy.
[…]
In its latest Ethiopia report, for example, the State Department identified significant human rights violations, including restrictions on freedom of speech, Stalinist-style show trials, and crackdowns on free press, opposition leaders, activists and critical journalists. The report and others by human rights groups reveal a consistent and widespread pattern of abuse, including torture, arbitrary killings, restrictions on freedom of association, interference in freedom of religion and the politicized use of the country’s anti-terrorism proclamation.
[…]
[Mass surveillance] and many other instruments of control enabled the EPRDF to win 99.6 percent of the votes in the 2010 elections, losing only two of the 547 seats in the federal Parliament and one seat out of the 1,900 in the regional assemblies. Five years of intimidation and harassment of the opposition and war against free press means that Sunday’s voting will be anything but fair and free.
Even more puzzling, as the country waits to see if other parties will win even two seats in the national parliament in Sunday’s elections, is the State Department’s odd assessment of trendlines in the country’s pseudo-democracy:
Speaking during a press briefing in Addis Ababa in April, Ms Sherman said: “Ethiopia is a democracy that is moving forward in an election that we expect to be free, fair and credible and open and inclusive in ways that Ethiopia has moved forward in strengthening its democracy. Every time there is an election it gets better and better.”
[…]
In 2005, 174 opposition politicians won seats in the 547-seat parliament, but many did not take them up after pronouncing the vote rigged.
In the 2010 polls, Girma Seifu, of the Unity for Democracy and Justice (UDJ), was the sole opponent to win, while the ruling EPRDF garnered 99.6% of all parliamentary seats. An independent candidate was also elected.
By definition, based on the past two elections, it has been getting worse. Perhaps it will be better this coming election, now that the country’s longtime dictator has passed away in the intervening time since the last election, but at the moment there’s no way to know that. And all signs don’t point to that at as a likely outcome.


