Investigative journalists at BuzzFeed put in a lot of hard work (and Freedom of Information requests) to uncover hundreds of deeply dubious authorizations last year for the sale and export of dual-use weapons to Turkey immediately following a violent government crackdown that began in late May 2013. The crackdown and clashes with protesters across the country resulted in the deaths of at least 11 people and injuries to literally more than 8,000 others.
The authorizations for the sale of controlled goods were made at a high level and almost no requests were denied despite the unfolding repressive response to the protests.
According to a Freedom of Information request made by BuzzFeed, the Department for Business Innovation and Skills granted multiple export licences to arms companies to export sniper rifles, bullets, gas masks, drone parts and other assorted military equipment to the country.
Ministers scrutinise the export of weapons, ammunition and other military technology to foreign countries and have to grant an explicit licence to companies looking to sell controlled goods.
Responding to the official request for information, the department told BuzzFeed that there had been 196 licences awarded by the UK government to firms since the clashes began in May, with only five requests refused.
The UK licenced over £90 million in military and dual-use licences to Turkey, according to the Campaign Against the Arms Trade.
It’s not unusual for the United Kingdom, the United States, or other manufacturers of advanced military and anti-riot hardware to sell to questionable governments — indeed there was heavy criticism that many of the tear gas canisters fired at protesters during the Arab Spring several years ago said “Made in the U.S.A.” in big letters.
And it’s also likely true most of the hardware being sold to Turkey last year was indeed for military use, rather than law enforcement use. That would separate it from the government and police, whose response last year was more or less separate from the erstwhile rivals in the Turkish Armed Forces. But a lot of it falls under the “dual-use” header, which means it could be used for a “legitimate” purpose but could also easily be used for a repressive or illegal purpose.
And, either way, selling it during and immediately following a crackdown (especially in a state where the military violently seized power as recently as 1980 before several more less successful attempts) seems like poor decision-making.
Moreover, poorly timed UK weapons sales to dubious governments in the region has not been limited to sales to this latest discovery. Just last September, a different journalistic investigation discovered horrifically worse sales had been authorized the year before (though fortunately were blocked externally in time). Here’s what I wrote last year:
Nearly a year into the brutal Syrian Civil War [in 2012], the British coalition government somehow decided to issue a license for a UK firm to export to Syria the chemical components used in sarin gas manufacturing. To a regime known to hold chemical weapons. In the middle of a civil war. The exports were only blocked by external, EU trade sanctions added 6 months later.
Granted, authorizing the sale of “dual-use” components that can be used to make chemical weapons, to a regime with just such a stockpile in the middle of a civil war, is an order of magnitude less explicable or justifiable than the Turkish deals.
And the UK government probably believes that there is no reason for it not to authorize weapons exports to a fellow founding member of NATO, Turkey, which is (a bit) more reliable than neighboring Syria.
We have no idea, according to BuzzFeed, whether the sales went through in this case, after authorization, because that’s proprietary information of the companies. But we do know that the licenses were granted and the Department for Business still doesn’t see a problem with it:
“The UK government takes its defence exports responsibilities extremely seriously and aims to operate one of the most robust export control systems in the world. All export licence applications are assessed thoroughly on a case-by-case basis against rigorous, internationally recognised criteria. If circumstances change, licensing decisions are reviewed quickly.”
Assessed thoroughly? If circumstances change, licensing decisions are reviewed quickly?
I mean, that’s an amazing claim to make from a government that had authorized weaponizable chemical sales to Syria the year before and then literally had the Prime Minister’s office declare that having the exports blocked only by the European Union’s intervention later with sanctions that didn’t exist earlier was “the system working.”
And the best part of that story is of course that the same UK government is trying to renegotiate its membership in the European Union before holding a deeply misguided referendum on whether or not to leave altogether.
Once outside the EU, I suppose, the United Kingdom will be free to export as many weapons to questionable states on the other perimeter of Europe to its heart’s content.
I’m sure Thatcher would be proud.
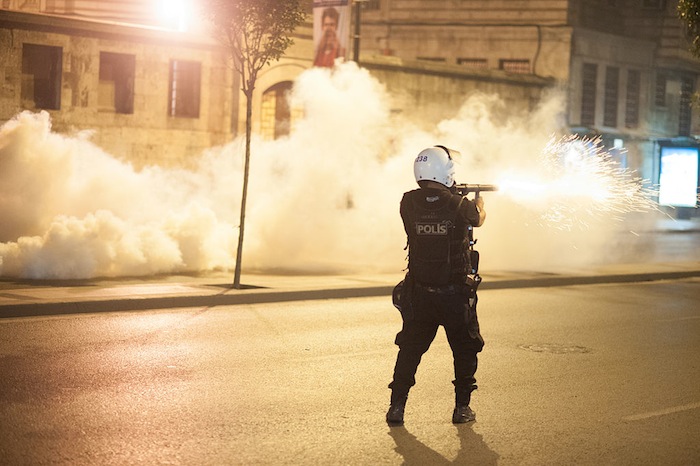

Riot police officer in action during Gezi park protests in Istanbul, June 16, 2013. (Credit: Mstyslav Chernov via Wikimedia)






 Sometimes the role of government isn’t about the really big things. Sometimes, it’s just about the little things that affect everything else.
Sometimes the role of government isn’t about the really big things. Sometimes, it’s just about the little things that affect everything else.