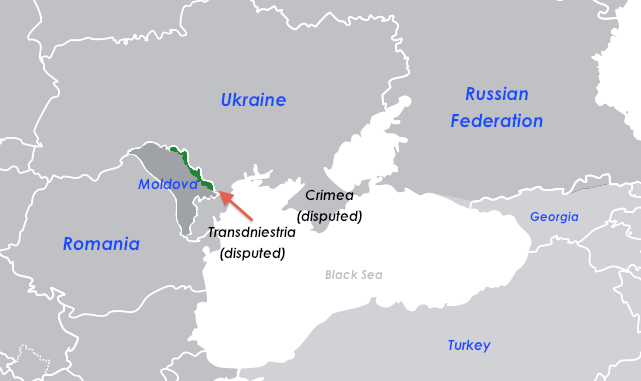
Obviously the simple answer to that question is a matter of when everyone officially agrees to stop disputing it, but that may never happen in some cases. So how do we balance the long-term geopolitical realities on the ground with the higher-level political concerns? That answer is not so easy.
Several weeks ago, I published a (disapproving) essay on National Geographic’s decision to transfer Crimea from Ukraine to Russia on its maps as soon as annexation occurred. Given the extremely contested circumstances surrounding the referendum to leave Ukraine, I felt this was overly hasty and risked reinforcing Russian claims without good reason, before the dust had even settled.
David Miller, a former Senior Editor at National Geographic, tweeted us his very compelling blog post on how (in the abstract, beyond National Geographic specifically) one makes a decision on how to map disputed territories, since it is indeed a bit subjective (as I had argued).
In “Crimea: A Map Controversy”, Miller notes the deep controversy over the referendum (held essentially at Russian gunpoint amid major boycotts), and then he lays out some factors to weigh deciding when it’s time to flip control on the map:
For accurate mapping of political sovereignty, the cartographer should consider four points: political claim, control of territory, international recognition of sovereignty, and time.
Let’s take them one at a time, as he does in the piece.
He observes that the governments of Ukraine and Russia both claim the territory. So it’s disputed, but anyone can dispute anything indefinitely, which means you have to look at the other factors.
He also observes that Russia must have military, political, and economic control of the region. It’s getting pretty close, but at the time National Geographic made its decision, the Ukrainian military hadn’t even evacuated the peninsula. It still hasn’t fully right now, I believe.
On the third point, he observes that there’s very little international recognition for this move and probably won’t be. Even Russian allies, such as Serbia, are hesitant to acknowledge the action for fear of de-legitimizing their own opposition to separatism and other neighborhood border disputes.
You rarely achieve resolution on all these points, but of course it’s about subjectively weighing them against each other before you color in the map.
Finally, the most subjective — and probably most important — factor to consider: time.
Time determines whether sovereignty is enduring or fleeting. Months or years may be necessary to judge a country’s claim and control of a region. For example, Morocco has claimed Western Sahara as a part of Morocco for decades, but its political control is limited and sovereignty is disputed. When Iraq invaded and annexed Kuwait in 1990, Iraqi sovereignty was disputed, and then it was overturned in 1991.
Outside the context of mapping, here’s another example that came to my mind on the issue of factoring in time: The U.S./U.N. abandoning its recognition of the Republic of China (ROC) in Taiwan as the “legitimate government” of mainland China, three decades after the ROC had lost control of the mainland to the People’s Republic of China (PRC).
Objectively, in that situation, there was no fundamental change on the ground or between the factions in 1979 that suddenly signaled that the PRC was more legitimate and permanent than it had been in, say, 1965. I’m sure certain political actions in the 1960s (such as the PRC’s brutal “Cultural Revolution”) probably didn’t help speed up U.S. recognition, but — other than Mao finally dying in 1976 — it probably wouldn’t have been any less arbitrary to normalize relations in 1960, 1965, 1972, etc.
All of which is to say sometimes in sovereignty disputes you really do just wait around to see how things play out and then one day you wake up and say to yourself “yeah, I think we better just accept this is the situation.”
That’s an definitely arbitrary and subjective solution, but at least giving a situation time ensures that it actually is going to remain that way rather than being reverse in a few more weeks. Crimea probably is going to remain Russian indefinitely and probably won’t be reversed back to Ukrainian control any time in the foreseeable future. But that doesn’t mean it’s time to change the color on the map to match Russia’s the second the referendum ends.
Miller’s verdict:
At this time, Crimea should be shown as disputed territory, which is usually a gray color on National Geographic maps with no sovereignty color.
But I do encourage everyone to read the full post, as I have only drawn a few bites out here and there, and he is a far more qualified person to speak on this subject than I am.
Thanks for sending it our way! If other readers also have articles/essays on the matter, let us know, or post a comment.
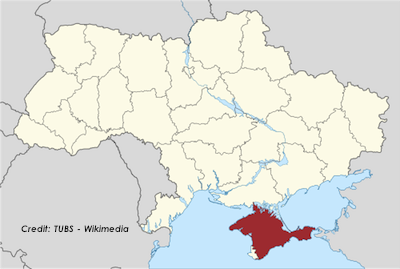







 The Crimea annexation has raised a crucial question: What is the world to do when a country with a large military and nuclear weapons decides to end a (voluntary, it turns out) period of non-aggression toward its neighbors?
The Crimea annexation has raised a crucial question: What is the world to do when a country with a large military and nuclear weapons decides to end a (voluntary, it turns out) period of non-aggression toward its neighbors?