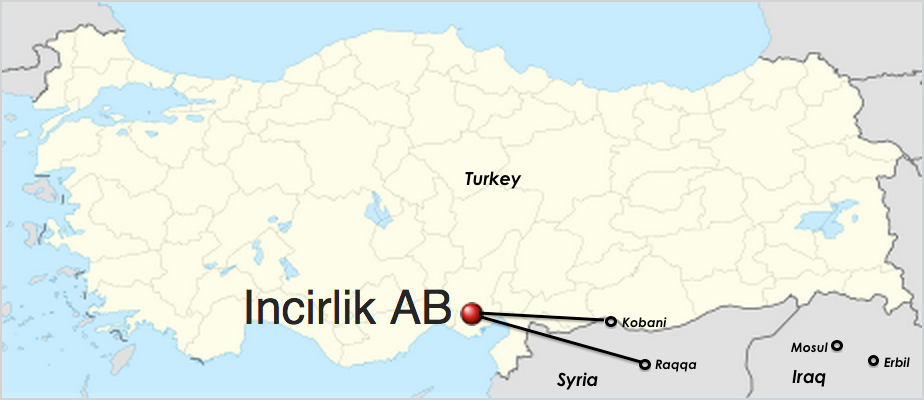
US cargo planes yesterday began ferrying supplies and ammunition from the Iraqi Kurdish Regional Government to Syrian Kurdish fighters in the besieged town of Kobani, despite protests from Turkey’s president.
Earlier Sunday, Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdogan said his country would not arm the Kurdish fighters, calling them “equal” to the Kurdistan Workers Party that both Turkey and the U.S. consider a terrorist group.
Erdogan said “it would be very, very wrong to expect” the Turkish government “to openly say ‘yes’ to our NATO ally America giving this kind of support. To expect something like this from us is impossible.”
This echoes the strident remarks made last weekend by Erdogan’s former deputy prime minister and the current number two in the president’s ruling AK Party, in which he asserted that the battle at Kobani was essentially just terrorists fighting terrorists. It also follows last week’s resumption of Turkish airstrikes against the PKK Kurdish fighters in Turkey after two years of peace.
That, combined with the embarrassing reversal on Turkish airbase use for the Syrian campaign a week ago, appears to have served as a breaking point for the United States on trying to placate Turkey on American policy on Syria’s Kurds, because there was another big shift in addition to the supply drops:
[Erdogan] made the comment days after the United States said it held its first direct talks with the Syrian Kurdish political party the Kurdish Democratic Union Party, which is tied to the Kurdish fighters in Kobani.
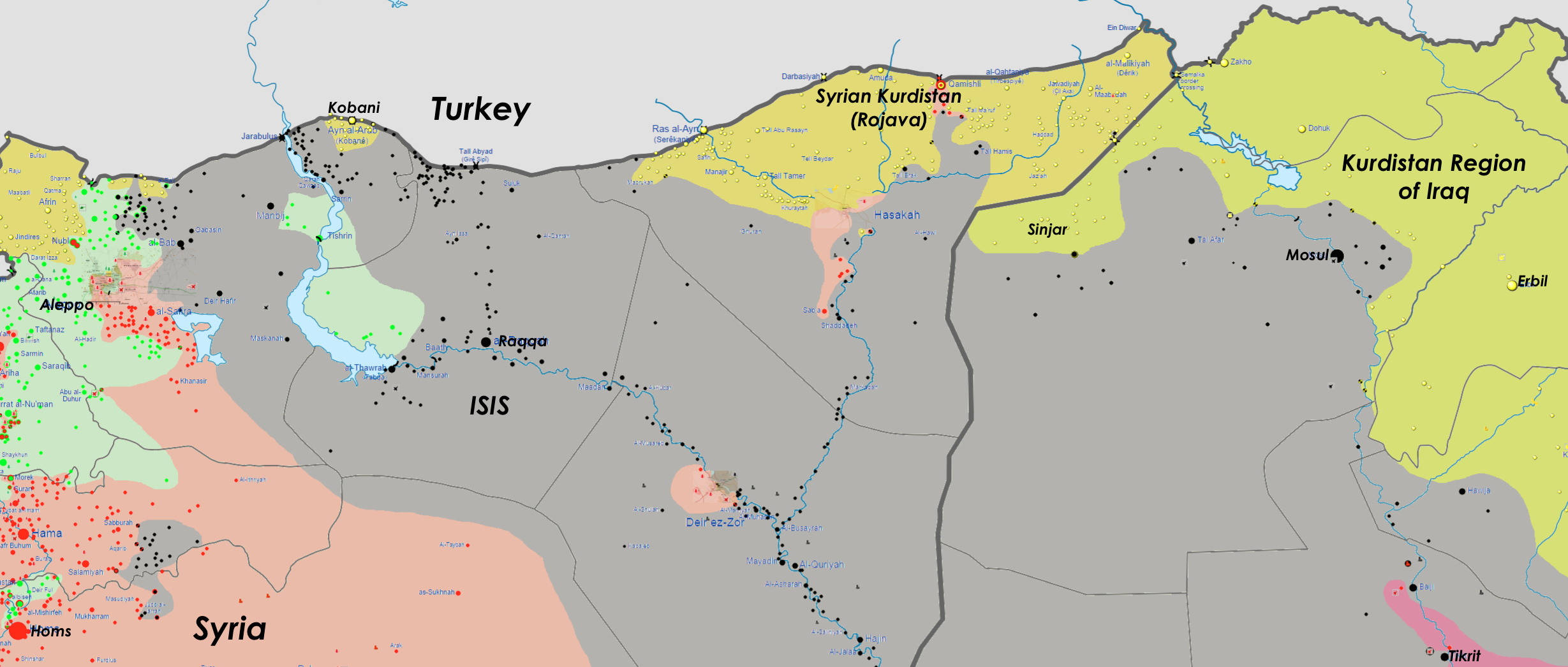
The Democratic Union Party (PYD) was formed in 2003 by the Syrian Kurdish backers of the PKK in Turkey, about five years after Syria’s Hafez al-Assad regime switched from supporting the the PKK to supporting the Turkish government and ejected the PKK from Syrian territory. During the current civil war, the PYD emerged as the central government structure of the increasingly independent Syrian Kurdistan in the country’s north, an area called “Rojava” or “Western Kurdistan” (eastern Kurdistan being the Iraqi and Iranian areas of Kurdish populations).
Because of their affiliation with the PKK against Turkey, the United States and the rival Kurdish political parties in Iraq had kept their distance from the PYD and their fighters (known as the YPG), but the threat of ISIS increasingly forced everyone toward a fork in the road on whether to embrace them or leave them behind. Turkey’s government appears to have taken the latter path, while the United States is choosing the former. (The Iraqi Kurdish Regional Government is still more on the fence. Despite yesterday’s aid to Kobani, they have complained as recently as last week that they don’t want to help the PYD because they might be allied with Bashar al-Assad, a dubious albeit vaguely plausible allegation that periodically circulates.)
Given the YPG’s vital help earlier this summer in relieving the ISIS siege of the Yazidis on Mount Sinjar in Iraq, helping the Kurdish fighters at Kobani is only fair. Moreover, the Kurdish paramilitaries in Syria remain one of the most reliably US-friendly militant groups in the country’s civil war, and the United States can ill afford to abandon any friends there now.
With the United States now directly talking to Kurdish leaders in Kobani in real time, coalition efforts to lift the siege at Kobani should make much more progress. As I noted previously, it seemed that Turkey’s obstruction and opposition to anyone coordinating with YPG fighters directly was a major impediment to military support at Kobani:
Not only has Turkey still not let coalition planes use airbases close to Kobani — which would make it much easier to reach to offer air support — but Turkey appears to be discouraging the US from talking to Syrian Kurd commanders on the ground to gain real-time intelligence. This may be why coalition airstrikes have been so limited and ineffective at Kobani: there are no spotters on the ground to report rapidly shifting targets for American planes. In contrast, the airstrikes have been much more effective in breaking Iraqi sieges at Sinjar and Amirli in part because the US has a much stronger and pre-existing, working relationship with the anti-ISIS commanders on the ground, particularly within Iraq’s Kurdish Regional Government’s paramilitaries.
The US, of course, is also more focused on broader strategic targets that will break ISIS overall, not just at Kobani […] But relief airstrikes have occurred in Iraq at several key points, which implies that if the United States had more ability to break the siege at Kobani, they would do so. A lot of that impediment seems to hinge on Turkey’s vacillation regarding how to handle the situation at Kobani (and its unwillingness to work with the Syrian Kurdish fighters or let the US work with them).
Already we have seen US airstrikes on ISIS at Kobani hit with more frequency and more accuracy in the past several days as YPG commanders provide targeting coordinates to American bombers.
We may well be witnessing the emergence of another far-reaching Middle Eastern alliance between the United States and a minority quasi-government with a large paramilitary.